Codebox Software
Rate Limited Web Service Library
Published:
This library provides a simple method for managing JavaScript access to rate-limited web services. The library is open-source and available on GitHub.
Many web-based services enforce usage limits, restricting how many service requests can be performed within a given period of time (for example at the time of writing, the Google Geocoding API permits 2,500 requests per 24 hour period for non-paying customers). By using this library to manage access to such a service, you can ensure that whatever limits have been imposed by the provider are never exceeded.
The library can manage multiple services at once, transparently load-balancing requests between them, so that whichever service has the largest usage quota remaining is the one that will be used.
An access strategy can be specified for each service, to determine how it will be managed.
- The Greedy Strategy will send as many requests to the service as possible, as quickly as possible, until the usage limit is reached. Once the limit has been reached no further requests will be sent until sufficient time has passed for the quota to be renewed.
- The Smoothing Strategy will attempt to distribute requests more evenly. Rather than considering the entire span of the rate-limited interval, it will divide the interval up into 'time buckets' and ensure that during each time bucket only the appropriate proportion of the quota is used.
The behaviors of the 2 strategies are illustrated in the diagram below, where multiple requests are made over a period of 1 minute, for a service that permits only 5 requests per minute. The vertical grey lines represent incoming requests, and the green ticks indicate which of those requests would be forwarded on to the service by each strategy:
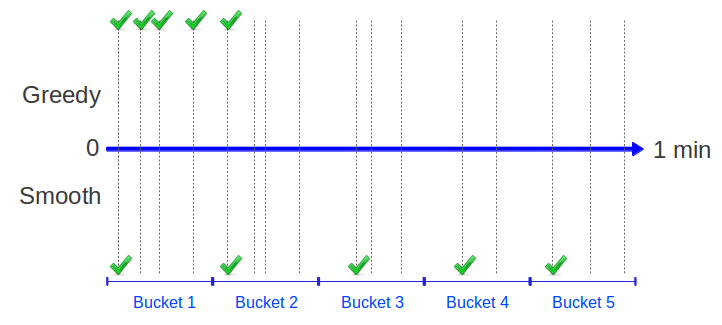
Obviously the Smoothing Strategy gives a much more uniform distribution of service calls over the interval, however it runs the risk of not fully utilising the available quota (for example, if there were no incoming requests for the final 2 time buckets, then 2 service requests out of the available 5 would be unused, effectively wasting them).
When multiple services are used, load-balancing is performed based on the proportion of the available quota which remains for each service (where the Smoothing Strategy is used), or on the priority assigned to each service (where the Greedy Strategy is used).
Example:
var manager = buildServiceManager();
var quota = manager.buildGreedyQuota(60, 100); // allow 100 requests per minute
manager.add(accessAllowed, quota);
// Some code somewhere else calls this when we want to use the remote service
function callTheServiceIfQuotaAllows(){
manager.call(undefined, accessDenied);
}
// These 2 functions are called by the library when it is determined that a request is to be allowed/disallowed
// from accessing the managed service
function accessAllowed(){
accessTheService();
log('request forwarded to service');
}
function accessDenied(){
log('request not forwarded to service');
}